Fichier:Protective barriers of the brain.jpg

Taille de cet aperçu : 442 × 599 pixels. Autres résolutions : 177 × 240 pixels | 567 × 768 pixels.
Fichier d’origine (567 × 768 pixels, taille du fichier : 356 kio, type MIME : image/jpeg)
Historique du fichier
Cliquer sur une date et heure pour voir le fichier tel qu'il était à ce moment-là.
| Date et heure | Vignette | Dimensions | Utilisateur | Commentaire | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| actuel | 22 septembre 2015 à 21:23 | 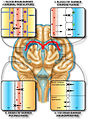 | 567 × 768 (356 kio) | Was a bee | {{Information |Description={{en|1=Protective barriers of the brain. The collective term “blood-brain barrier” is used to describe four main interfaces between the central nervous system and the periphery. (i) The blood-brain barrier proper formed b... |
Utilisation du fichier
La page suivante utilise ce fichier :
Usage global du fichier
Les autres wikis suivants utilisent ce fichier :
- Utilisation sur ar.wikipedia.org
- Utilisation sur bn.wikipedia.org
- Utilisation sur bs.wikipedia.org
- Utilisation sur ca.wikipedia.org
- Utilisation sur en.wikipedia.org
- Utilisation sur eu.wikipedia.org
- Utilisation sur fi.wiktionary.org
- Utilisation sur lv.wikipedia.org
- Utilisation sur sr.wikipedia.org
- Utilisation sur th.wikipedia.org
- Utilisation sur tr.wikipedia.org
- Utilisation sur www.wikidata.org
- Utilisation sur zh.wikipedia.org
